Introduction
In our interconnected digital landscape, cybersecurity has evolved into an essential component of business strategy. Every organization possesses its own valuable assets; some prioritize safeguarding customer Personally Identifiable Information (PII), while others place great value on protecting their Intellectual Property (IP). In the race of innovation and with the growing occurrence of supply chain cyber-attacks, it is equally imperative for organizations to fortify their security posture.
For most startups, operating as digital natives and conducting business primarily over the internet is the norm. Startups play a crucial role in addressing key challenges for large enterprises, however, in comparison to well-established enterprises, startups often have less mature cybersecurity defenses, making them attractive targets for cybercriminals.
Why is a robust cybersecurity strategy crucial for startups?
In contrast to larger enterprises, startups operate with limited budgets for cybersecurity. Given the rapid pace of innovation and intense competitiveness in the business landscape, a well-crafted cybersecurity strategy is an essential element within a startup’s business blueprint. This strategy serves to safeguard valuable data, build confidence, maintain compliance, and mitigate potential risks, all of which collectively bolster the startup’s ability to thrive and adapt in an ever-changing digital environment.
So, what should be the right cybersecurity strategy for startups to ensure balance between business, security and at the same time being cost effective? Below are the key points to be considered while defining cybersecurity strategy for your startup:
- Acknowledge that your startup can be a potential target for cyber threats and proactively identify your specific vulnerabilities.
- Identify and prioritize quick-win security measures, such as strengthening password protection, effective patch management, securing APIs, and implementing encryption.
- Distinguish between cybersecurity functions that can be managed in-house and those that are better outsourced to experts.
- Ensure the security of your cloud resources and establish secure connectivity, incorporating tools like Web Application Firewalls (WAF), Virtual Private Networks (VPN), and IP, port, and MAC binding.
- Bolster endpoint security to protect all devices connected to your network.
- Implement stringent access control mechanisms, adhering to the principle of least privilege to restrict unauthorized access.
- Carefully evaluate the risks associated with adopting open-source tools before integrating them into your infrastructure.
- Foster a strong cybersecurity culture within your organization, emphasizing that “cybersecurity is everyone’s responsibility.”
- Establish well-documented policies and processes for cybersecurity, including a comprehensive incident response strategy.
- Identify high risk vendors and adopt robust vendor risk management.
How we have approached for cybersecurity at Shiprocket:
At Shiprocket, we prioritize cybersecurity as our top concern. Our management is deeply committed to establishing a secure digital environment. We’ve embraced a risk-based approach that is gradually integrated across technology, processes, and people.
- “The People” strategy: We have adopted a hybrid approach in formulating Information Security team as shown below:
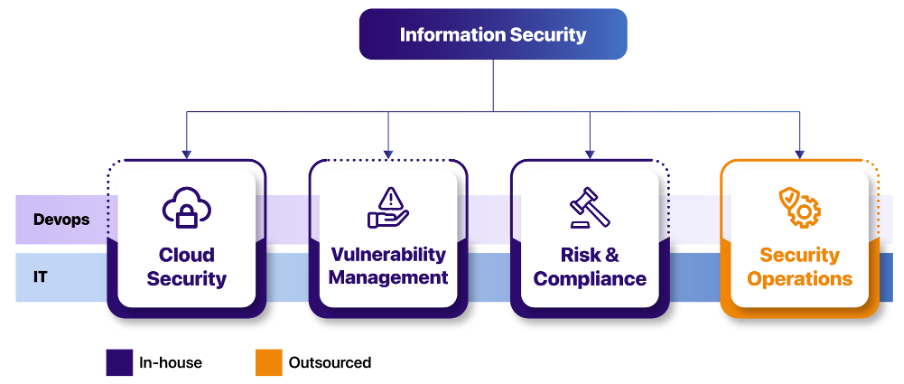
- Fungible team members for cloud security and vulnerability management teams.
- Organic growth of team.
- Mentor-mentee culture to foster a culture of cross learning.
- Shared responsibility between information security team, developers, IT and DevOps.
- “The Technology” strategy: We have a heterogeneous mix of enterprise tools and open-source tools. The methodology for tool selection is as below:
- Tried open-source tools to validate the use cases and adopted enterprise tools wherever required.
- Adopted a platform-based approach over multiple tools operating in silos.
- Chosen interoperable tools and automated as much as possible.
- Secure cloud, secure APIs and secure endpoints are non-negotiable.
- “The Process” strategy: We initiated by comprehending the business and operational methods, then incorporated secure practices into the current operating model. The methodology is outlined below:
- Explored industry leading security standards and selected one which aligns the most.
- Socialize the policies and processes with all the stakeholders.
- Drive adoption of policies and practices in collaboration with key stakeholders.
- Continuous compliance monitoring and remediation.
Key Takeaways:
- The information security strategy should be devised considering factors such as risk, compliance obligations, and the specific sector of customers being served.
- Encourage the active participation of senior management in executing the information security strategy.
- Adopt a phase-wise journey for implementing security controls and ensuring healthy adoption of security practices across the organization.
- Promote the idea that “Security is a shared responsibility”.
- Achieve the right blend of enterprise tools and open-source solutions to ensure both effectiveness and agility.
- Identify high risk vendors and ensure their risks are appropriately mitigated.
- Implement Continuous Compliance Monitoring for proactive risk management.
- Adopt an interoperable platform instead of multiple isolated point-in-time tools.
- Regularly review the information security strategy to ensure its relevance in a highly innovative and dynamic environment.